手多汗症
手多汗症
手掌過度出汗 (手掌多汗症) 是一種常見的疾病,約有百分之一至四的人口受其影響 [1,2] 。這種情況會影響工作和社交生活。簡單如處理文件的工作亦可能成為問題,重要的社交禮儀如握手亦變得尷尬,令患者盡量迥避這些互動。
非手術治療
不幸地,非手術代表不會做得很好,非手術治療包括:
1. 應用止汗濟,一般無效。如用含有氯化鋁的止汗濟,可能會有輕微短暫的效果, 長期使用可引至皮膚問題。
2. 抗膽鹼類藥物:減少全身整體出汗而並非專減手掌。副作用很普遍。
3. 電離子導入法:一般無效,或是只有部份和短暫的效果。
4. 注射肉毒桿菌:有效,但在手掌注射是非常痛苦的,效果只可持續三至四個月,需要重複注射[3] 。
手術治療
利用胸椎交感神經切除術可令手掌達至永久乾爽。以往,這手術並不普及,因為當時它屬於開放式的大手術, 而且手術風險相當高,例如傷及臂叢神經,星狀神經節和肺部 [4,5,6] 。對於一個相對「良性」的病情而言,開放式手術的規模及風險都很大,因此很多醫生都不鼓勵患者進行此手術。不過時至今日,胸椎交感神經切除術可通過微創技術進行,令風險減至最低 [7,8,9] 。
胸腔鏡交感神經切除術或內窺鏡胸椎交感神經切除術是透過望遠鏡在手術位置提供清晰的影像。術後通常 只留下兩或三個近乎無痛的小傷口 (圖 1 和 2)。
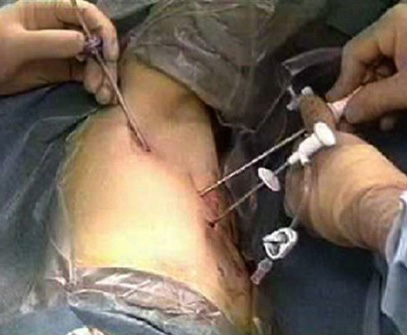 圖1 三個二至三毫米的小傷口用來進行胸腔鏡交感神經切除術下。 |
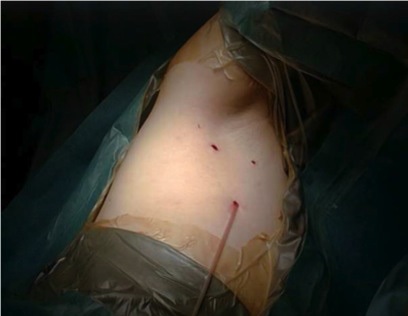 圖2 術後的傷口。手術完結前會用小導管吸走傷口內的所有空氣,因此不需使用胸腔引流。 |
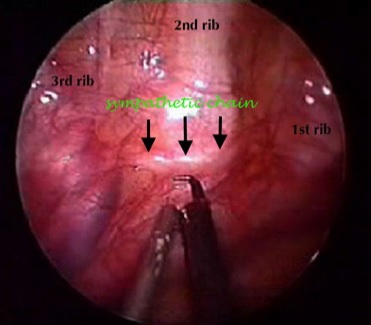
在胸腔鏡下,可以清楚分辨交感神經鏈,從而分割或切除部分神經 (圖 3 和 4)。
|
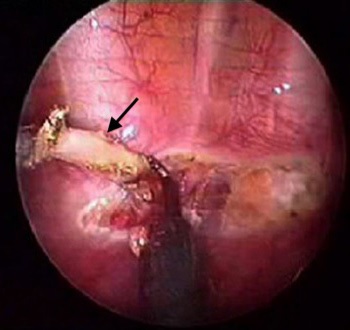 圖4 交感神經鏈 (箭咀所指) 從胸壁被切開。 |
最近的研究顯示,在第三肋骨之上把交感神經鏈分割,可獲得最高的成功率 [9,10] 。換言之,術後雙手變得乾爽的成功率是接近百分之一百 (圖 5) [7,9,11] 。
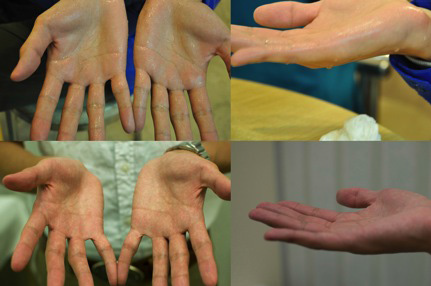 圖5 同一患者於術前的手掌 (上圖) 與接受交感神經切除術後三週的手掌 (下圖)。術後的手掌完全乾爽。注意術後的手因血管擴張而變得紅潤。 |
手術後大約有六至七成患者會出現代償性出汗 12。大多數的代償性出汗屬於輕微,只有百分之五至十的個案是嚴重[13,14] 。只要限制交感神經切除的範圍,便可能減輕代償性出汗的發生率。
由於胸腔鏡技術能提供清晰影像,可避免損害星狀神經節,亦因此大大減少霍納氏症候群 (眼瞼下垂,瞳孔縮小和臉部無汗) 的發生[7,8] 。作者近三百個交感神經切除個案中,沒有出現過霍納氏症候群 (個人數據)。
其他術後併發症包括肺部出血和損傷,但由經驗豐富的醫生處理的個案中並不常見 [11,14] 。此手術多可作日間手術進行 [15,16,17] 。
結論
以現代的胸腔鏡交感神經切除術治療手多汗症,成功率已接近百分之一百。手術風險低且術後併發症通常很輕微。加上傷口細小,不會影響儀容。所以對於長期受手多汗症困擾的人來說,此治療方法是高度推介的。
參考文獻
1. Haider A, Solish N. Focal hyperhidrosis: diagnosis and management. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2005;172(1):69-75.
2. Strutton DR, Kowalski J, Glaser DA, Stang P. US prevalence of hyperhidrosis: results from a national consumer panel. Poster presentation at the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology 2003; Poster abstract P362, San Francisco, Calif
3. Ambrosia V, Campione E, Mieo D et al. Bilateral thoracoscopic T2 to T3 sympathectomy versus botulinum injection in palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorax Surg 2009 Jul;88(1):238-45.
4. Little JM, May J. A comparison of supraclavicular and axillary approaches to upper thoracic sympathectomy. Aust NZ J Surg 1975;45:143-6.
5. Kurchin A, Zweig A, Adar R, Mozes M. Upper dorsal sympathectomy for palmar primary hyperhidrosis by the supraclavicular approach. World J Surg 1977;1:667-74.
6. Adar R, Kurchin A, Zweig A, Mozes M. Palmar hyperhidrosis and its surgical treatment: a report of 100 cases. Ann Surg 1977;186:34-41.
7. Tai YP, Lee MWM, Li MKW. Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: Hong Kong early experience. HK Med J 1996;2(3):315-8.
8. Li X, Tu YR, Lin M et al. Minimizing endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis: guided by palmar skin temperature and laser Doppler blood flow. Ann Thorac Surg 2009 Feb;87(2):427-31.
9. Deng B, Tan QY, Jiang YG et al. Optimization of sympathectomy to treat palmar hyperhidrosis: the systemic review and meta-analysis of studies published during the past decade. Surg Endosc 2011 Jun;25(6):1893-901.
10. Cerfolio RJ, De Campos JR, Bryant AS et al. The society of thoracic surgeons expert consensus for the surgical treatment of hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 2011 May;91(5):1642-8.
11. Liu Y, Yang J, Liu J et al. Surgical treatment of primary hyperhidrosis: a prospective randomized study comparing T3 and T4 sympathicotomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2009 Mar;35(3):398-402.
12. Araujo CA, Axevedo IM, Ferreira MA et al. Compensatory sweating after thoracoscopic sympathectomy: characteristics, prevalence and influence on patient satisfaction. J Bras Pneumol 2009 Mar;35(3):213-20.
13. Li X, Tu YR, Lin M et al. Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a randomized control trial comparing T3 and T2-4 ablation. Ann Thorac Surg 2008 May;85(5):1747-51.
14. Rodriguez PM, Freixinet JL, Hussein M et al. Side effects, complications and outcome of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis in 406 patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2008 Sep;34(3):514-9.
15. Cameron A. Early experience with day-case transthoracic endoscopic sympathectomy. Br J Surg 1999 Jan;86(1):139.
16. Hsia JY, Chen CY, Hsu CP et al. Outpatient thoracoscopic limited sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis palmaris. Ann Thorac Surg 1999 Jan;67(1)258-9.
17. Miller DL, Force SD. Outpatient microthoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 2007 May;83(5):1850-3.
此文章原文由亞洲專科醫生以英文撰寫 © 2017 亞洲專科醫生有限公司,版權所有 |